Automation Opportunities for Medical Device Companies are Wide Open

“Guaranteeing safety in automated processes is not just a question of human responsibility but also of economic sense.” (Werner von Siemens – 1880)
For years, the aerospace, automotive, chemicals/ plastics, pharmaceuticals, consumer and electronics industries have employed automation technology to increase productivity and reduce manufacturing costs. Since then, automation in medical has come into the spotlight as well.
Although the growth of robotics was interrupted by the financial crisis of 2009, it has resumed with earnest, especially with recent emphasis on manufacturing innovation and reshoring. According to the International Federation of Robotics, in 2011, robot sales jumped 38 percent to 166,028 units, by far the highest level ever recorded for one year.
Interestingly, the use of robotics in medical device manufacturing occurs for some niche applications. However, the presence of automation in medical may not be as ubiquitous as in other industries. Automation systems are often very product specific. Because system design and operations are optimized for the production of a specific family of parts, such as automobiles, printed circuit boards, deodorants, etc., these machines provide consistent quality at potentially high production rates but are not flexible enough to accommodate completely different designs, which are often the case with medical devices.
Subscribe to the Jabil Blog
Sign up for weekly updates on the latest trends, research and insight in tech, IoT and the supply chain.
Robot-Based Automation
Dedicated manufacturing solutions are often expensive investments and may require significant expenditure when modifications are required to accommodate changes in product design. It is not uncommon for a completely new system to be designed when new products are introduced. To meet commercial pressures, device manufacturers are turning to robot-based automation systems that can provide throughput, quality and consistency along with flexibility to accommodate different designs.
Robotics can provide the capability to process different products through the same system and are reconfigurable for new products, thereby reducing costs and improving delivery flexibility. The case for such integrated automation in medical is becoming increasingly compelling as medical device manufacturers face greater cost pressures and shorter product lifecycles.
Considerations for Adopting Medical Device Automation
Device developers put a great deal of time and energy into the design of a new medical product. However, with their focus on the functional features and performance of the design, they may overlook the need to consider manufacturing requirements, including assembly, especially if the product is expected to reach millions in volumes as in single use devices. With the move to robotics, designing for automation becomes imperative – mainly because of the constraints of the regulatory process. Once agency approval is secured, it can be difficult to go back and make even minor modifications to a design and or the manufacturing process. Any changes may require revalidation and/or significant internal documentation for a failure risk analysis.
Another important consideration is selection of the automation system provider who will analyze your automation system needs; provide a plan for robotic system integration; support equipment validation and qualification; and facilitate launching and servicing the automation system through production. In any case, the medical device manufacturer must clearly communicate requirements, including tasks that the robots will perform, rate of throughput and quality standards such as tolerances.
One area of automation in medical is the cleanroom – a topic of strong interest in view of the current focus on infection control. Also, for cost reasons, an aseptic environment within the manufacturing process is desirable to produce sterilized products without a secondary sterilization step. People must undergo an intensive cleaning process every time they enter an aseptic environment clean room. Robots remain in place and do not typically move in and out of assembly area, avoiding the risk of transporting pollutants. However, they may require significant upfront investment and maintenance because of the special low-dust and low-debris parts used in dust-proof enclosures.
Another area is packaging of devices. The risk analysis required to determine acceptable reconfiguration of a robotic system handling packaging is less complicated than that involved in the reconfiguration of medical device assembly. Therefore it may be easier to receive robotic intervention in this area.
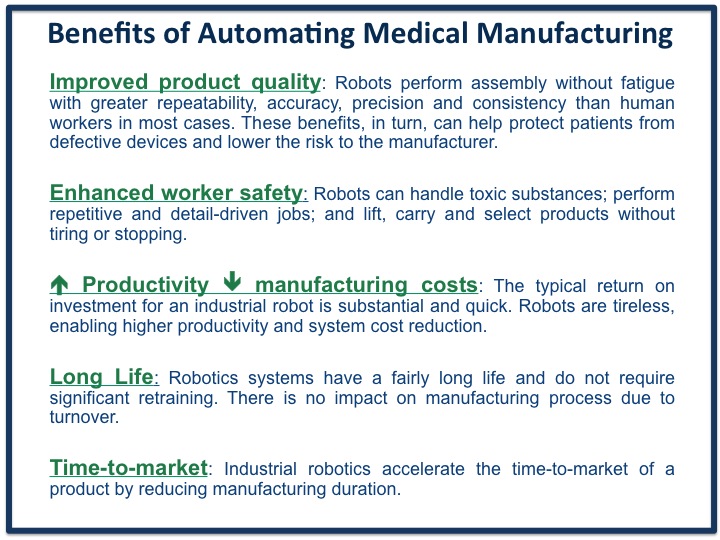
The use of robotics in all area of manufacturing will continue to grow with opportunities for medical device automation remaining wide open. Robotic systems help companies achieve their goals while at the same time reducing overall manufacturing costs.
Is your company using automation today or are you still on the fence on whether robot integration is for you?
Learn why Jabil is the leading provider of medical design and manufacturing solutions.